The structures of the anti-tuberculosis antibiotics viomycin and capreomycin bound to the 70S ribosome
- PMID: 20154709
- PMCID: PMC2917106
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.1755
The structures of the anti-tuberculosis antibiotics viomycin and capreomycin bound to the 70S ribosome
Abstract
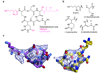
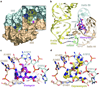
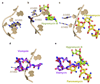
Viomycin and capreomycin belong to the tuberactinomycin family of antibiotics, which are among the most effective antibiotics against multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. Here we present two crystal structures of the 70S ribosome in complex with three tRNAs and bound to either viomycin or capreomycin at 3.3- and 3.5-A resolution, respectively. Both antibiotics bind to the same site on the ribosome, which lies at the interface between helix 44 of the small ribosomal subunit and helix 69 of the large ribosomal subunit. The structures of these complexes suggest that the tuberactinomycins inhibit translocation by stabilizing the tRNA in the A site in the pretranslocation state. In addition, these structures show that the tuberactinomycins bind adjacent to the binding sites for the paromomycin and hygromycin B antibiotics, which may enable the development of new derivatives of tuberactinomycins that are effective against drug-resistant strains.
Figures
References
-
- Guy ES, Mallampalli A. Managing TB in the 21st century: existing and novel drug therapies. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2008;2:401–408. - PubMed
-
- WHO. Global Tuberculosis Control: Epidemology, Strategy, Financing: WHO report 2009. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2009. p. 314.
-
- Yamada T, Mizugichi Y, Nierhaus KH, Wittmann HG. Resistance to viomycin conferred by RNA of either ribosomal subunit. Nature. 1978;275:460–461. - PubMed
Methods
-
- Perona JJ, Swanson R, Steitz TA, Soll D. Overproduction and purification of Escherichia coli tRNA(2Gln) and its use in crystallization of the glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase-tRNA(Gln) complex. Journal of Molecular Biology. 1988;202:121–126. - PubMed
-
- Kabsch W. XDS. In: Rossmann MG, Arnold E, editors. International Tables in Crystallography. Vol. F. Dordrecht, Netherlands: Published for the International Union of Crystallography by Springer; 2005. pp. 730–734.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

