Structure and function of a genetically engineered mimic of a nonenveloped virus entry intermediate
- PMID: 20164221
- PMCID: PMC2863772
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02670-09
Structure and function of a genetically engineered mimic of a nonenveloped virus entry intermediate
Abstract
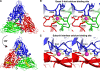
Divalent metal ions are components of numerous icosahedral virus capsids. Flock House virus (FHV), a small RNA virus of the family Nodaviridae, was utilized as an accessible model system with which to address the effects of metal ions on capsid structure and on the biology of virus-host interactions. Mutations at the calcium-binding sites affected FHV capsid stability and drastically reduced virus infectivity, without altering the overall architecture of the capsid. The mutations also altered the conformation of gamma, a membrane-disrupting, virus-encoded peptide usually sequestered inside the capsid, by increasing its exposure under neutral pH conditions. Our data demonstrate that calcium binding is essential for maintaining a pH-based control on gamma exposure and host membrane disruption, and they reveal a novel rationale for the metal ion requirement during virus entry and infectivity. In the light of the phenotypes displayed by a calcium site mutant of FHV, we suggest that this mutant corresponds to an early entry intermediate formed in the endosomal pathway.
Figures
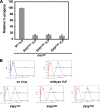

References
-
- Adamec, T., Z. Palkova, K. Velkova, J. Stokrova, and J. Forstova. 2005. Point mutation in calcium-binding domain of mouse polyomavirus VP1 protein does not prevent virus-like particle formation, but changes VP1 interactions with Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell structures. FEMS Yeast Res. 5:331-340. - PubMed
-
- Aramayo, R., C. Merigoux, E. Larquet, P. Bron, J. Perez, C. Dumas, P. Vachette, and N. Boisset. 2005. Divalent ion-dependent swelling of tomato bushy stunt virus: a multi-approach study. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1724:345-354. - PubMed
-
- Arias-Moreno, X., A. Velazquez-Campoy, J. C. Rodriguez, M. Pocovi, and J. Sancho. 2008. Mechanism of low density lipoprotein (LDL) release in the endosome: implications of the stability and Ca2+ affinity of the fifth binding module of the LDL receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 283:22670-22679. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee, M., and J. E. Johnson. 2008. Activation, exposure and penetration of virally encoded, membrane-active polypeptides during non-enveloped virus entry. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 9:16-27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

