Structural insight into dynamic bypass of the major cisplatin-DNA adduct by Y-family polymerase Dpo4
- PMID: 20512114
- PMCID: PMC2892363
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2010.101
Structural insight into dynamic bypass of the major cisplatin-DNA adduct by Y-family polymerase Dpo4
Abstract
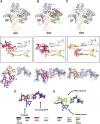
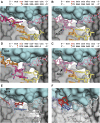
Y-family DNA polymerases bypass Pt-GG, the cisplatin-DNA double-base lesion, contributing to the cisplatin resistance in tumour cells. To reveal the mechanism, we determined three structures of the Y-family DNA polymerase, Dpo4, in complex with Pt-GG DNA. The crystallographic snapshots show three stages of lesion bypass: the nucleotide insertions opposite the 3'G (first insertion) and 5'G (second insertion) of Pt-GG, and the primer extension beyond the lesion site. We observed a dynamic process, in which the lesion was converted from an open and angular conformation at the first insertion to a depressed and nearly parallel conformation at the subsequent reaction stages to fit into the active site of Dpo4. The DNA translocation-coupled conformational change may account for additional inhibition on the second insertion reaction. The structures illustrate that Pt-GG disturbs the replicating base pair in the active site, which reduces the catalytic efficiency and fidelity. The in vivo relevance of Dpo4-mediated Pt-GG bypass was addressed by a dpo-4 knockout strain of Sulfolobus solfataricus, which exhibits enhanced sensitivity to cisplatin and proteomic alterations consistent with genomic stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Albertella MR, Green CM, Lehmann AR, O'Connor MJ (2005) A role for polymerase eta in the cellular tolerance to cisplatin-induced damage. Cancer Res 65: 9799–9806 - PubMed
-
- Allen MB (1959) Studies with Cyanidium caldarium, an anomalously pigmented chlorophyte. Arch Mikrobiol 32: 270–277 - PubMed
-
- Alt A, Lammens K, Chiocchini C, Lammens A, Pieck JC, Kuch D, Hopfner KP, Carell T (2007) Bypass of DNA lesions generated during anticancer treatment with cisplatin by DNA polymerase eta. Science 318: 967–970 - PubMed
-
- Bassett E, Vaisman A, Havener JM, Masutani C, Hanaoka F, Chaney SG (2003) Efficiency of extension of mismatched primer termini across from cisplatin and oxaliplatin adducts by human DNA polymerases beta and eta in vitro. Biochemistry 42: 14197–14206 - PubMed
-
- Bassett E, Vaisman A, Tropea KA, McCall CM, Masutani C, Hanaoka F, Chaney SG (2002) Frameshifts and deletions during in vitro translesion synthesis past Pt-DNA adducts by DNA polymerases beta and eta. DNA Repair (Amst) 1: 1003–1016 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

