Coumarinyl-substituted sulfonamides strongly inhibit several human carbonic anhydrase isoforms: solution and crystallographic investigations
- PMID: 20598552
- PMCID: PMC2950089
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmc.2010.06.028
Coumarinyl-substituted sulfonamides strongly inhibit several human carbonic anhydrase isoforms: solution and crystallographic investigations
Abstract
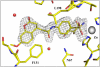
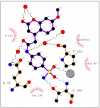
We investigated a series of coumarinyl-substituted aromatic sulfonamides as inhibitors of four carbonic anhydrase (CA, EC 4.2.1.1) isoforms with medical applications, the cytosolic hCA I, and II, and the transmembrane, tumor-associated hCA IX and XII. Compounds incorporating 7-methoxy-coumarin-4-yl-acetamide-tails and benzenesulfonamide and benzene-1,3-disulfonamide scaffolds showed medium potency inhibition of hCA I (KIs of 73-131 nM), effective hCA II inhibition (KIs of 9.1-36 nM) and less effective hCA IX and XII inhibition (KIs of 55-128 nM). Only one compound, the derivatized 4-amino-6-trifluoromethyl-benzene-1,3-disulfonamide with the coumarinyl tail, showed effective inhibition of the transmembrane isoforms, with KIs of 5.9-14.2 nM, although it was less effective as hCA I and II inhibitor (KIs of 36-120 nM). An X-ray crystal structure of hCA II in complex with 4-(7-methoxy-coumarin-4-yl-acetamido)-benzenesulfonamide (KI of 9.1 nM against hCA II) showed the intact inhibitor coordinated to the zinc ion from the enzyme active site by the sulfonamide moiety, and participating in a edge-to-face stacking with Phe131, in addition to other hydrophobic and hydrophilic interactions with water molecules and amino acid residues from the active site. Thus, sulfonamides incorporating coumarin rings have a distinct inhibition mechanism compared to the coumarins, and may lead to compounds with interesting inhibition profiles against various alpha-CAs found in mammals or parasites, such as Plasmodium falciparum.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Supuran CT. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008;7:168. - PubMed
- Supuran CT, Scozzafava A, Casini A. Development of sulfonamide carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (CAIs) In: Supuran CT, Scozzafava A, Conway J, editors. Carbonic anhydrase – Its Inhibitors and Activators. CRC Press; Boca Raton (FL): 2004. pp. 67–147.
- Domsic JF, Avvaru BS, Kim CU, Gruner SM, Agbandje-McKenna M, Silverman DN, McKenna R. J. Biol. Chem. 2008;283:30766. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Supuran CT. Carbonic anhydrases as drug targets – general presentation. In: Supuran CT, Winum JY, editors. Drug Design of Zinc-Enzyme Inhibitors: Functional, Structural, and Disease Applications. Wiley; Hoboken (NJ): 2009. pp. 15–38.
- Winum JY, Rami M, Scozzafava A, Montero JL, Supuran C. Med. Res. Rev. 2008;28:445. - PubMed
- Supuran CT, Scozzafava A, Casini A. Med. Res. Rev. 2003;23:146. - PubMed
-
- Nair SK, Ludwig PA, Christianson DW. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994;116:3659.
- Innocenti A, Vullo D, Scozzafava A, Supuran CT. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008;18:1583. - PubMed
- Innocenti A, Hilvo M, Scozzafava A, Parkkila S, Supuran CT. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008;18:3593–3596. - PubMed
- Innocenti A, Vullo D, Scozzafava A, Supuran CT. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008;16:7424. - PubMed
- Barrese AA, 3rd, Genis C, Fisher SZ, Orwenyo JN, Kumara MT, Dutta SK, Phillips E, Kiddle JJ, Tu C, Silverman DN, Govindasamy L, Agbandje-McKenna M, McKenna R, Tripp BC. Biochemistry. 2008;47:3174. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information

