The E3 ubiquitin ligase- and protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A)-binding domains of the Alpha4 protein are both required for Alpha4 to inhibit PP2A degradation
- PMID: 21454489
- PMCID: PMC3093842
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.222414
The E3 ubiquitin ligase- and protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A)-binding domains of the Alpha4 protein are both required for Alpha4 to inhibit PP2A degradation
Abstract
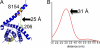
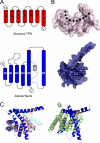
Protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) is regulated through a variety of mechanisms, including post-translational modifications and association with regulatory proteins. Alpha4 is one such regulatory protein that binds the PP2A catalytic subunit (PP2Ac) and protects it from polyubiquitination and degradation. Alpha4 is a multidomain protein with a C-terminal domain that binds Mid1, a putative E3 ubiquitin ligase, and an N-terminal domain containing the PP2Ac-binding site. In this work, we present the structure of the N-terminal domain of mammalian Alpha4 determined by x-ray crystallography and use double electron-electron resonance spectroscopy to show that it is a flexible tetratricopeptide repeat-like protein. Structurally, Alpha4 differs from its yeast homolog, Tap42, in two important ways: 1) the position of the helix containing the PP2Ac-binding residues is in a more open conformation, showing flexibility in this region; and 2) Alpha4 contains a ubiquitin-interacting motif. The effects of wild-type and mutant Alpha4 on PP2Ac ubiquitination and stability were examined in mammalian cells by performing tandem ubiquitin-binding entity precipitations and cycloheximide chase experiments. Our results reveal that both the C-terminal Mid1-binding domain and the PP2Ac-binding determinants are required for Alpha4-mediated protection of PP2Ac from polyubiquitination and degradation.
© 2011 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures




References
-
- Kong M., Bui T. V., Ditsworth D., Gruber J. J., Goncharov D., Krymskaya V. P., Lindsten T., Thompson C. B. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282, 29712–29720 - PubMed
-
- Kong M., Fox C. J., Mu J., Solt L., Xu A., Cinalli R. M., Birnbaum M. J., Lindsten T., Thompson C. B. (2004) Science 306, 695–698 - PubMed
-
- Goedert M., Jakes R., Qi Z., Wang J. H., Cohen P. (1995) J. Neurochem. 65, 2804–2807 - PubMed
-
- Eichhorn P. J., Creyghton M. P., Bernards R. (2009) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1795, 1–15 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

