Structural basis of peptide recognition by the angiotensin-1 converting enzyme homologue AnCE from Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 23082758
- PMCID: PMC3564407
- DOI: 10.1111/febs.12038
Structural basis of peptide recognition by the angiotensin-1 converting enzyme homologue AnCE from Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
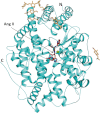
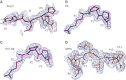
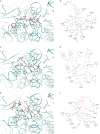
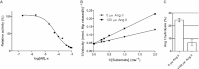
Human somatic angiotensin-1 converting enzyme (ACE) is a zinc-dependent exopeptidase, that catalyses the conversion of the decapeptide angiotensin I to the octapeptide angiotensin II, by removing a C-terminal dipeptide. It is the principal component of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system that regulates blood pressure. Hence it is an important therapeutic target for the treatment of hypertension and cardiovascular disorders. Here, we report the structures of an ACE homologue from Drosophila melanogaster (AnCE; a proven structural model for the more complex human ACE) co-crystallized with mammalian peptide substrates (bradykinin, Thr(6) -bradykinin, angiotensin I and a snake venom peptide inhibitor, bradykinin-potentiating peptide-b). The structures determined at 2-Å resolution illustrate that both angiotensin II (the cleaved product of angiotensin I by AnCE) and bradykinin-potentiating peptide-b bind in an analogous fashion at the active site of AnCE, but also exhibit significant differences. In addition, the binding of Arg-Pro-Pro, the cleavage product of bradykinin and Thr(6) - bradykinin, provides additional detail of the general peptide binding in AnCE. Thus the new structures of AnCE complexes presented here improves our understanding of the binding of peptides and the mechanism by which peptides inhibit this family of enzymes.
Database: The atomic coordinates and structure factors for AnCE-Ang II (code 4AA1), AnCE-BPPb (code 4AA2), AnCE-BK (code 4ASQ) and AnCE-Thr6-BK (code 4ASR) complexes have been deposited in the Protein Data Bank, Research Collaboratory for Structural Bioinformatics, Rutgers University, New Brunswick, NJ (http://www.rcsb.org/)
Structured digital abstract: • AnCE cleaves Ang I by enzymatic study (View interaction) • Bradykinin and AnCE bind by x-ray crystallography (View interaction) • BPP and AnCE bind by x-ray crystallography (View interaction) • AnCE cleaves Bradykinin by enzymatic study (View interaction) • Ang II and AnCE bind by x-ray crystallography (View interaction).
© 2012 The Authors Journal compilation © 2012 FEBS.
Figures

References
-
- Corvol P, Eyries M, Soubrier F. Peptidyl-dipeptidase A/angiotensin I-converting enzyme. In: Barrett AJ, Rawlings ND, Woessner JF, editors. Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes. San Diego: Elsevier Academic Press; 2004. pp. 332–346.
-
- Ondetti MA, Cushman DW. Enzymes of the renin–angiotensin system and their inhibitors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:283–308. - PubMed
-
- Anthony CS, Masuyer G, Sturrock ED, Acharya KR. Structure-based drug design of angiotensin-1 converting enzyme. Curr Med Chem. 2012;19:845–855. - PubMed
-
- Wei L, Alhenc-Gelas F, Corvol P, Clauser E. The two homologous domains of human angiotensin I-converting enzyme are both catalytically active. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:9002–9008. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

