Molecular mechanism of ligand recognition by membrane transport protein, Mhp1
- PMID: 24952894
- PMCID: PMC4195764
- DOI: 10.15252/embj.201387557
Molecular mechanism of ligand recognition by membrane transport protein, Mhp1
Abstract
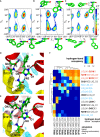
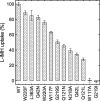
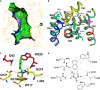
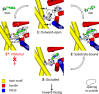
The hydantoin transporter Mhp1 is a sodium-coupled secondary active transport protein of the nucleobase-cation-symport family and a member of the widespread 5-helix inverted repeat superfamily of transporters. The structure of Mhp1 was previously solved in three different conformations providing insight into the molecular basis of the alternating access mechanism. Here, we elucidate detailed events of substrate binding, through a combination of crystallography, molecular dynamics, site-directed mutagenesis, biochemical/biophysical assays, and the design and synthesis of novel ligands. We show precisely where 5-substituted hydantoin substrates bind in an extended configuration at the interface of the bundle and hash domains. They are recognised through hydrogen bonds to the hydantoin moiety and the complementarity of the 5-substituent for a hydrophobic pocket in the protein. Furthermore, we describe a novel structure of an intermediate state of the protein with the external thin gate locked open by an inhibitor, 5-(2-naphthylmethyl)-L-hydantoin, which becomes a substrate when leucine 363 is changed to an alanine. We deduce the molecular events that underlie acquisition and transport of a ligand by Mhp1.
Keywords: Mhp1; five helix inverted repeat superfamily; hydantoin; membrane transport; molecular recognition; nucleobase‐cation‐symport, NCS1, family.
© 2014 The Authors. Published under the terms of the CC BY 4.0 license.
Figures


References
-
- Altenbuchner J, Siemann-Herzberg M, Syldatk C. Hydantoinases and related enzymes as biocatalysts for the synthesis of unnatural chiral amino acids. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2001;12:559–563. - PubMed
-
- Bommarius AS, Schwarm M, Drauz K. Biocatalysis to amino acid-based chiral pharmaceuticals - examples and perspectives. J Mol Catalysis B-Enzymatic. 1998;5:1–11.
-
- Broer S, Palacin M. The role of amino acid transporters in inherited and acquired diseases. Biochem J. 2011;436:193–211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- BB/L002558/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/C51725/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BBS/B/16011/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- B19456/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/G020043/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/H000267/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/I019855/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BEP17032/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT089809/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- BB/G023425/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- BB/C51725X/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

