The CDK9 tail determines the reaction pathway of positive transcription elongation factor b
- PMID: 22959624
- PMCID: PMC3469819
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2012.08.011
The CDK9 tail determines the reaction pathway of positive transcription elongation factor b
Abstract
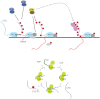
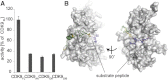
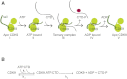
CDK9, the kinase of positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb), stimulates transcription elongation by phosphorylating RNA polymerase II and transcription elongation factors. Using kinetic analysis of a human P-TEFb complex consisting of CDK9 and cyclin T, we show that the CDK9 C-terminal tail sequence is important for the catalytic mechanism and imposes an ordered binding of substrates and release of products. Crystallographic analysis of a CDK9/cyclin T complex in which the C-terminal tail partially blocks the ATP binding site reveals a possible reaction intermediate. Biochemical characterization of CDK9 mutants supports a model in which the CDK9 tail cycles through different conformational states. We propose that this mechanism is critical for the pattern of CTD Ser2 phosphorylation on actively transcribed genes.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Adams J.A. Kinetic and catalytic mechanisms of protein kinases. Chem. Rev. 2001;101:2271–2290. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

