The ABC-F protein EttA gates ribosome entry into the translation elongation cycle
- PMID: 24389466
- PMCID: PMC4101993
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.2740
The ABC-F protein EttA gates ribosome entry into the translation elongation cycle
Abstract
ABC-F proteins have evaded functional characterization even though they compose one of the most widely distributed branches of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) superfamily. Herein, we demonstrate that YjjK, the most prevalent eubacterial ABC-F protein, gates ribosome entry into the translation elongation cycle through a nucleotide-dependent interaction sensitive to ATP/ADP ratio. Accordingly, we rename this protein energy-dependent translational throttle A (EttA). We determined the crystal structure of Escherichia coli EttA and used it to design mutants for biochemical studies including enzymological assays of the initial steps of protein synthesis. These studies suggest that EttA may regulate protein synthesis in energy-depleted cells, which have a low ATP/ADP ratio. Consistently with this inference, EttA-deleted cells exhibit a severe fitness defect in long-term stationary phase. These studies demonstrate that an ABC-F protein regulates protein synthesis via a new mechanism sensitive to cellular energy status.
Figures

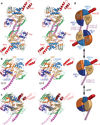

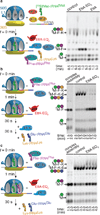
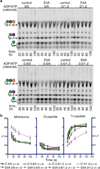


Comment in
-
The ABCs of the ribosome.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2014 Feb;21(2):115-6. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2765. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24500425 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Cavanaugh LF, Palmer AG, 3rd, Gierasch LM, Hunt JF. Disorder breathes life into a DEAD motor. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006;13:566–569. - PubMed
-
- Jones PM, George AM. Subunit interactions in ABC transporters: towards a functional architecture. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1999;179:187–202. - PubMed
-
- Hopfner KP, et al. Structural biology of Rad50 ATPase: ATP-driven conformational control in DNA double-strand break repair and the ABC-ATPase superfamily. Cell. 2000;101:789–800. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- GM074958/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM029169/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM074958/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM055440/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008281/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM55440/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 GM084288/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM029169/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM29169/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P41 GM111244/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- MOP 114938/CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- U54 GM094597/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM084288/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

