Unusual base pairing during the decoding of a stop codon by the ribosome
- PMID: 23812587
- PMCID: PMC3732562
- DOI: 10.1038/nature12302
Unusual base pairing during the decoding of a stop codon by the ribosome
Abstract
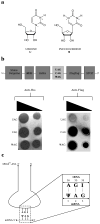
During normal translation, the binding of a release factor to one of the three stop codons (UGA, UAA or UAG) results in the termination of protein synthesis. However, modification of the initial uridine to a pseudouridine (Ψ) allows efficient recognition and read-through of these stop codons by a transfer RNA (tRNA), although it requires the formation of two normally forbidden purine-purine base pairs. Here we determined the crystal structure at 3.1 Å resolution of the 30S ribosomal subunit in complex with the anticodon stem loop of tRNA(Ser) bound to the ΨAG stop codon in the A site. The ΨA base pair at the first position is accompanied by the formation of purine-purine base pairs at the second and third positions of the codon, which show an unusual Watson-Crick/Hoogsteen geometry. The structure shows a previously unsuspected ability of the ribosomal decoding centre to accommodate non-canonical base pairs.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions

