Crystal structures of EF-G-ribosome complexes trapped in intermediate states of translocation
- PMID: 23812722
- PMCID: PMC3979973
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1236086
Crystal structures of EF-G-ribosome complexes trapped in intermediate states of translocation
Abstract
Translocation of messenger and transfer RNA (mRNA and tRNA) through the ribosome is a crucial step in protein synthesis, whose mechanism is not yet understood. The crystal structures of three Thermus ribosome-tRNA-mRNA-EF-G complexes trapped with β,γ-imidoguanosine 5'-triphosphate (GDPNP) or fusidic acid reveal conformational changes occurring during intermediate states of translocation, including large-scale rotation of the 30S subunit head and body. In all complexes, the tRNA acceptor ends occupy the 50S subunit E site, while their anticodon stem loops move with the head of the 30S subunit to positions between the P and E sites, forming chimeric intermediate states. Two universally conserved bases of 16S ribosomal RNA that intercalate between bases of the mRNA may act as "pawls" of a translocational ratchet. These findings provide new insights into the molecular mechanism of ribosomal translocation.
Figures
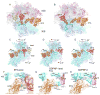
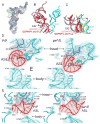
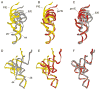
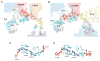
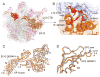
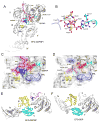
Comment in
-
Biochemistry. Translocation in action.Science. 2013 Jun 28;340(6140):1534-5. doi: 10.1126/science.1240090. Science. 2013. PMID: 23812707 No abstract available.
References
-
- Moazed D, Noller HF. Nature. 1989;342:142. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

