X-ray crystal structures of the Escherichia coli RNA polymerase in complex with benzoxazinorifamycins
- PMID: 23679862
- PMCID: PMC3745299
- DOI: 10.1021/jm4004889
X-ray crystal structures of the Escherichia coli RNA polymerase in complex with benzoxazinorifamycins
Abstract
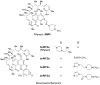
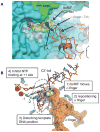
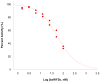
Rifampin, a semisynthetic rifamycin, is the cornerstone of current tuberculosis treatment. Among many semisynthetic rifamycins, benzoxazinorifamycins have great potential for TB treatment due to their superior affinity for wild-type and rifampin-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis RNA polymerases and their reduced hepatic Cyp450 induction activity. In this study, we have determined the crystal structures of the Escherichia coli RNA polymerase complexes with two benzoxazinorifamycins. The ansa-naphthalene moieties of the benzoxazinorifamycins bind in a deep pocket of the β subunit, blocking the path of the RNA transcript. The C3'-tail of benzoxazinorifamycin fits a cavity between the β subunit and σ factor. We propose that in addition to blocking RNA exit, the benzoxazinorifamycin C3'-tail changes the σ region 3.2 loop position, which influences the template DNA at the active site, thereby reducing the efficiency of transcription initiation. This study supports expansion of structure-activity relationships of benzoxazinorifamycins inhibition of RNA polymerase toward uncovering superior analogues with development potential.
Figures
References
-
- World-Health-Organization. WHO Report 2011: Global Tuberculosis Control. 2011.
-
- Siddiqi MI, Kumar A. Review of knowledge for rational design and identification of anti-tubercular compounds. Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery. 2009;4:1005–1015. - PubMed
-
- Lienhardt C, Vernon A, Raviglione MC. New drugs and new regimens for the treatment of tuberculosis: review of the drug development pipeline and implications for national programmes. Current Opinion in Pulmonary Medicine. 2010;16:186–193. - PubMed
-
- Aristoff PA, Garcia GA, Kirchhoff PD, Showalter HD. Rifamycins – Obstacles and Opportunities. Tuberculosis. 2010;90:94–118. - PubMed
-
- Telenti A, Imboden P, Marchesi F, Lowrie D, Cole S, Colston J, Matter L, Schopfer K, Bodmer T. Detection of rifampicin-resistance mutation in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Lancet. 1993;341:647–650. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Miscellaneous

