The mechanism of pseudouridine synthases from a covalent complex with RNA, and alternate specificity for U2605 versus U2604 between close homologs
- PMID: 24214967
- PMCID: PMC3919597
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt1050
The mechanism of pseudouridine synthases from a covalent complex with RNA, and alternate specificity for U2605 versus U2604 between close homologs
Abstract
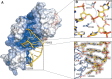
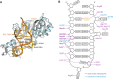
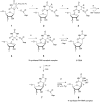
RluB catalyses the modification of U2605 to pseudouridine (Ψ) in a stem-loop at the peptidyl transferase center of Escherichia coli 23S rRNA. The homolog RluF is specific to the adjacent nucleotide in the stem, U2604. The 1.3 Å resolution crystal structure of the complex between the catalytic domain of RluB and the isolated substrate stem-loop, in which the target uridine is substituted by 5-fluorouridine (5-FU), reveals a covalent bond between the isomerized target base and tyrosine 140. The structure is compared with the catalytic domain alone determined at 2.5 Å resolution. The RluB-bound stem-loop has essentially the same secondary structure as in the ribosome, with a bulge at A2602, but with 5-FU2605 flipped into the active site. We showed earlier that RluF induced a frame-shift of the RNA, moving A2602 into the stem and translating its target, U2604, into the active site. A hydrogen-bonding network stabilizes the bulge in the RluB-RNA but is not conserved in RluF and so RluF cannot stabilize the bulge. On the basis of the covalent bond between enzyme and isomerized 5-FU we propose a Michael addition mechanism for pseudouridine formation that is consistent with all experimental data.
Figures




References
-
- Bjork G. Stable RNA Modification. In: Neidhardt FC, Curtiss R, editors. Escherichia coli and Salmonella: Cellular and Molecular Biology. 2nd edn. Washington, DC: ASM Press; 1996. pp. 861–886.
-
- Moore PB, Steitz TA. The involvement of RNA in ribosome function. Nature. 2002;418:229–235. - PubMed
-
- Ofengand J. Ribosomal RNA pseudouridines and pseudouridine synthases. FEBS Lett. 2002;514:17–25. - PubMed
-
- Huang L, Pookanjanatavip M, Gu X, Santi DV. A conserved aspartate of tRNA pseudouridine synthase is essential for activity and a probable nucleophilic catalyst. Biochemistry. 1998;37:344–351. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

