Structure of zebrafish IRBP reveals fatty acid binding
- PMID: 26344741
- PMCID: PMC4624502
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2015.08.026
Structure of zebrafish IRBP reveals fatty acid binding
Abstract
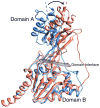
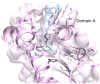
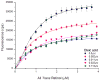
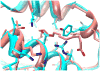
Interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein (IRBP) has a remarkable role in targeting and protecting all-trans and 11-cis retinol, and 11-cis retinal during the rod and cone visual cycles. Little is known about how the correct retinoid is efficiently delivered and removed from the correct cell at the required time. It has been proposed that different fatty composition at that the outer-segments and retinal-pigmented epithelium have an important role is regulating the delivery and uptake of the visual cycle retinoids at the cell-interphotoreceptor-matrix interface. Although this suggests intriguing mechanisms for the role of local fatty acids in visual-cycle retinoid trafficking, nothing is known about the structural basis of IRBP-fatty acid interactions. Such regulation may be mediated through IRBP's unusual repeating homologous modules, each containing about 300 amino acids. We have been investigating structure-function relationships of Zebrafish IRBP (zIRBP), which has only two tandem modules (z1 and z2), as a model for the more complex four-module mammalian IRBP's. Here we report the first X-ray crystal structure of a teleost IRBP, and the only structure with a bound ligand. The X-ray structure of z1, determined at 1.90 Å resolution, reveals a two-domain organization of the module (domains A and B). A deep hydrophobic pocket with a single bound molecule of oleic acid was identified within the N-terminal domain A. In fluorescence titrations assays, oleic acid displaced all-trans retinol from zIRBP. Our study, which provides the first structure of an IRBP with bound ligand, supports a potential role for fatty acids in regulating retinoid binding.
Keywords: Interphotoreceptor matrix; Interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein; Oleic acid; RBP3; Retina; Visual cycle; X-ray structure; Zebrafish.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures




References
-
- Adler AJ, Stafford WF, 3rd, Slayter HS. Size and shape of bovine interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein by electron microscopy and hydrodynamic analysis. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:13198–13203. - PubMed
-
- Allison WT, Haimberger TJ, Hawryshyn CW, Temple SE. Visual pigment composition in zebrafish: Evidence for a rhodopsin-porphyropsin interchange system. Vis Neurosci. 2004;21:945–952. - PubMed
-
- Arno G, Hull S, Robson AG, Holder GE, Cheetham ME, Webster AR, Plagnol V, Moore AT. Lack of interphotoreceptor retinoid binding protein, caused by homozygous mutation of RBP3, is associated with high myopia and retinal dystrophy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2015 - PubMed
-
- Baer CA, Retief JD, Van Niel E, Braiman MS, Gonzalez-Fernandez F. Soluble expression in E. coli of a functional interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein module fused to thioredoxin: correlation of vitamin A binding regions with conserved domains of C-terminal processing proteases. Exp Eye Res. 1998a;66:249–262. - PubMed
-
- Baer CA, Van Niel EE, Cronk JW, Kinter MT, Sherman NE, Braiman MS, Gonzalez-Fernandez F. Arginine to glutamine substitutions in the fourth module of Xenopus interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein. Mol Vis. 1998b;4:30–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

