A highly conserved cysteine of neuronal calcium-sensing proteins controls cooperative binding of Ca2+ to recoverin
- PMID: 24189072
- PMCID: PMC3861663
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.524355
A highly conserved cysteine of neuronal calcium-sensing proteins controls cooperative binding of Ca2+ to recoverin
Abstract
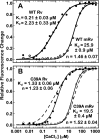
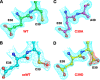
Recoverin, a 23-kDa Ca(2+)-binding protein of the neuronal calcium sensing (NCS) family, inhibits rhodopsin kinase, a Ser/Thr kinase responsible for termination of photoactivated rhodopsin in rod photoreceptor cells. Recoverin has two functional EF hands and a myristoylated N terminus. The myristoyl chain imparts cooperativity to the Ca(2+)-binding sites through an allosteric mechanism involving a conformational equilibrium between R and T states of the protein. Ca(2+) binds preferentially to the R state; the myristoyl chain binds preferentially to the T state. In the absence of myristoylation, the R state predominates, and consequently, binding of Ca(2+) to the non-myristoylated protein is not cooperative. We show here that a mutation, C39A, of a highly conserved Cys residue among NCS proteins, increases the apparent cooperativity for binding of Ca(2+) to non-myristoylated recoverin. The binding data can be explained by an effect on the T/R equilibrium to favor the T state without affecting the intrinsic binding constants for the two Ca(2+) sites.
Keywords: Allosteric Regulation; Calcium Signaling; Calcium-binding Proteins; Cooperativity; Cysteine; Mutant; Neuronal Calcium Sensor; Protein Myristoylation; Sulfenic Acid.
Figures





References
-
- Klenchin V. A., Calvert P. D., Bownds M. D. (1995) Inhibition of rhodopsin kinase by recoverin: further evidence for a negative feedback system in phototransduction. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 16147–16152 - PubMed
-
- Chen C. K., Inglese J., Lefkowitz R. J., Hurley J. B. (1995) Ca2+-dependent interaction of recoverin with rhodopsin kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 18060–18066 - PubMed
-
- Higgins M. K., Oprian D. D., Schertler G. F. (2006) Recoverin binds exclusively to an amphipathic peptide at the N terminus of rhodopsin kinase, inhibiting rhodopsin phosphorylation without affecting catalytic activity of the kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 19426–19432 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

