Prokaryotic NavMs channel as a structural and functional model for eukaryotic sodium channel antagonism
- PMID: 24850863
- PMCID: PMC4060673
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1406855111
Prokaryotic NavMs channel as a structural and functional model for eukaryotic sodium channel antagonism
Abstract
Voltage-gated sodium channels are important targets for the development of pharmaceutical drugs, because mutations in different human sodium channel isoforms have causal relationships with a range of neurological and cardiovascular diseases. In this study, functional electrophysiological studies show that the prokaryotic sodium channel from Magnetococcus marinus (NavMs) binds and is inhibited by eukaryotic sodium channel blockers in a manner similar to the human Nav1.1 channel, despite millions of years of divergent evolution between the two types of channels. Crystal complexes of the NavMs pore with several brominated blocker compounds depict a common antagonist binding site in the cavity, adjacent to lipid-facing fenestrations proposed to be the portals for drug entry. In silico docking studies indicate the full extent of the blocker binding site, and electrophysiology studies of NavMs channels with mutations at adjacent residues validate the location. These results suggest that the NavMs channel can be a valuable tool for screening and rational design of human drugs.
Keywords: crystal structure; pharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
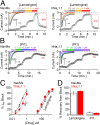

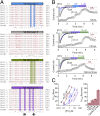
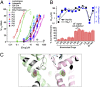
References
-
- Catterall WA, Goldin AL, Waxman SG. International Union of Pharmacology. XLVII. Nomenclature and structure-function relationships of voltage-gated sodium channels. Pharmacol Rev. 2005;57(4):397–409. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- T32 HL007572/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- BB/L006790/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- P30 HD018655/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- BB/J020702/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- T32-HL007572/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

