The chromosome axis controls meiotic events through a hierarchical assembly of HORMA domain proteins
- PMID: 25446517
- PMCID: PMC4254552
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2014.09.013
The chromosome axis controls meiotic events through a hierarchical assembly of HORMA domain proteins
Abstract
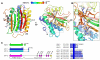
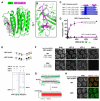
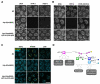
Proteins of the HORMA domain family play central, but poorly understood, roles in chromosome organization and dynamics during meiosis. In Caenorhabditis elegans, four such proteins (HIM-3, HTP-1, HTP-2, and HTP-3) have distinct but overlapping functions. Through combined biochemical, structural, and in vivo analysis, we find that these proteins form hierarchical complexes through binding of their HORMA domains to cognate peptides within their partners' C-terminal tails, analogous to the "safety belt" binding mechanism of Mad2. These interactions are critical for recruitment of HIM-3, HTP-1, and HTP-2 to chromosome axes. HTP-3, in addition to recruiting the other HORMA domain proteins to the axis, plays an independent role in sister chromatid cohesion and double-strand break formation. Finally, we find that mammalian HORMAD1 binds a motif found both at its own C terminus and at that of HORMAD2, indicating that this mode of intermolecular association is a conserved feature of meiotic chromosome structure in eukaryotes.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Comment in
-
HORMA domains at the heart of meiotic chromosome dynamics.Dev Cell. 2014 Nov 24;31(4):389-91. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2014.11.009. Epub 2014 Nov 24. Dev Cell. 2014. PMID: 25458007
References
-
- Aravind L, Koonin EV. The HORMA domain: a common structural denominator in mitotic checkpoints, chromosome synapsis and DNA repair. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1998;23:284–286. - PubMed
-
- Blat Y, Protacio RU, Hunter N, Kleckner N. Physical and functional interactions among basic chromosome organizational features govern early steps of meiotic chiasma formation. Cell. 2002;111:791–802. - PubMed
-
- Caryl AP, Armstrong SJ, Jones GH, Franklin FC. A homologue of the yeast HOP1 gene is inactivated in the Arabidopsis meiotic mutant asy1. Chromosoma. 2000;109:62–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

