Dimerization of lipocalin allergens
- PMID: 26346541
- PMCID: PMC4561914
- DOI: 10.1038/srep13841
Dimerization of lipocalin allergens
Abstract
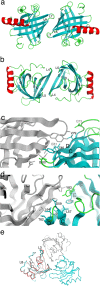
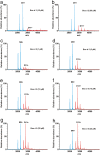
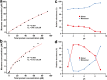
Lipocalins are one of the most important groups of inhalant animal allergens. The analysis of structural features of these proteins is important to get insights into their allergenicity. We have determined two different dimeric crystal structures for bovine dander lipocalin Bos d 2, which was earlier described as a monomeric allergen. The crystal structure analysis of all other determined lipocalin allergens also revealed oligomeric structures which broadly utilize inherent structural features of the β-sheet in dimer formation. According to the moderate size of monomer-monomer interfaces, most of these dimers would be transient in solution. Native mass spectrometry was employed to characterize quantitatively transient dimerization of two lipocalin allergens, Bos d 2 and Bos d 5, in solution.
Conflict of interest statement
M.N., J.J. and J.R. are shareholders of Desentum Oy. The rest of the authors declare that they have no relevant conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Gould H. J. & Sutton B. J. IgE in allergy and asthma today. Nature Rev. Immunol. 8, 205–217 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Virtanen T., Kinnunen T. & Rytkönen-Nissinen M. Mammalian lipocalin allergens—insights into their enigmatic allergenicity. Clin. Exp. Allergy 42, 494–504 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Hilger C. et al. IgE-mediated anaphylaxis caused by bites of the pigeon tick Argas reflexus: Cloning and expression of the major allergen Arg r 1. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 115, 617–622 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

