Chemical Tools To Decipher Regulation of Phosphatases by Proline Isomerization on Eukaryotic RNA Polymerase II
- PMID: 26332362
- PMCID: PMC4788383
- DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.5b00296
Chemical Tools To Decipher Regulation of Phosphatases by Proline Isomerization on Eukaryotic RNA Polymerase II
Abstract
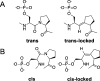
Proline isomerization greatly impacts biological signaling but is subtle and difficult to detect in proteins. We characterize this poorly understood regulatory mechanism for RNA polymerase II carboxyl terminal domain (CTD) phosphorylation state using novel, direct, and quantitative chemical tools. We determine the proline isomeric preference of three CTD phosphatases: Ssu72 as cis-proline specific, Scp1 and Fcp1 as strongly trans-preferred. Due to this inherent characteristic, these phosphatases respond differently to enzymes that catalyze the isomerization of proline, like Ess1/Pin1. We demonstrate that this selective regulation of RNA polymerase II phosphorylation state exists within human cells, consistent with in vitro assays. These results support a model in which, instead of a global enhancement of downstream enzymatic activities, proline isomerases selectively boost the activity of a subset of CTD regulatory factors specific for cis-proline. This leads to diversified phosphorylation states of CTD in vitro and in cells. We provide the chemical tools to investigate proline isomerization and its ability to selectively enhance signaling in transcription and other biological contexts.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures





References
-
- Eick D, Geyer M. The RNA polymerase II carboxyterminal domain (CTD) code. Chem Rev (Washington, DC, US) 2013;113:8456–8490. - PubMed
-
- Bataille AR, Jeronimo C, Jacques PE, Laramee L, Fortin ME, Forest A, Bergeron M, Hanes SD, Robert F. A universal RNA polymerase II CTD cycle is orchestrated by complex interplays between kinase, phosphatase, and isomerase enzymes along genes. Mol Cell. 2012;45:158–170. - PubMed
-
- Schroder S, Herker E, Itzen F, He D, Thomas S, Gilchrist DA, Kaehlcke K, Cho S, Pollard KS, Capra JA, Schnolzer M, Cole PA, Geyer M, Bruneau BG, Adelman K, Ott M. Acetylation of RNA polymerase II regulates growth-factor-induced gene transcription in mammalian cells. Mol Cell. 2013;52:314–324. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Conaway JW, Shilatifard A, Dvir A, Conaway RC. Control of elongation by RNA polymerase II. Trends Biochem Sci. 2000;25:375–380. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

