Crystal Structures of the Extracellular Domain from PepT1 and PepT2 Provide Novel Insights into Mammalian Peptide Transport
- PMID: 26320580
- PMCID: PMC4597091
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2015.07.016
Crystal Structures of the Extracellular Domain from PepT1 and PepT2 Provide Novel Insights into Mammalian Peptide Transport
Abstract
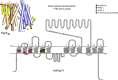
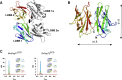
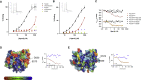
Mammals obtain nitrogen via the uptake of di- and tri-peptides in the gastrointestinal tract through the action of PepT1 and PepT2, which are members of the POT family of proton-coupled oligopeptide transporters. PepT1 and PepT2 also play an important role in drug transport in the human body. Recent crystal structures of bacterial homologs revealed a conserved peptide-binding site and mechanism of transport. However, a key structural difference exists between bacterial and mammalian homologs with only the latter containing a large extracellular domain, the function of which is currently unknown. Here, we present the crystal structure of the extracellular domain from both PepT1 and PepT2 that reveal two immunoglobulin-like folds connected in tandem, providing structural insight into mammalian peptide transport. Functional and biophysical studies demonstrate that these domains interact with the intestinal protease trypsin, suggesting a role in clustering proteolytic activity to the site of peptide transport in eukaryotic cells.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures




Comment in
-
Digesting New Elements in Peptide Transport.Structure. 2015 Oct 6;23(10):1779-1780. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2015.09.006. Structure. 2015. PMID: 26445489
References
-
- Abrahams J.P., Leslie A.G.W. Methods used in the structure determination of bovine mitochondrial F1 ATPase. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 1996;52:30–42. - PubMed
-
- Adibi S.A. The oligopeptide transporter (Pept-1) in human intestine: biology and function. Gastroenterology. 1997;113:332–340. - PubMed
-
- Adibi S.A. Renal assimilation of oligopeptides: physiological mechanisms and metabolic importance. Am. J. Physiol. 1997;272:E723–E736. - PubMed
-
- Ashida K., Katsura T., Motohashi H., Saito H., Inui K. Thyroid hormone regulates the activity and expression of the peptide transporter PEPT1 in Caco-2 cells. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2002;282:G617–G623. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

