A Novel Fucose-binding Lectin from Photorhabdus luminescens (PLL) with an Unusual Heptabladed β-Propeller Tetrameric Structure
- PMID: 27758853
- PMCID: PMC5122772
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.693473
A Novel Fucose-binding Lectin from Photorhabdus luminescens (PLL) with an Unusual Heptabladed β-Propeller Tetrameric Structure
Abstract
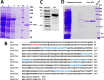
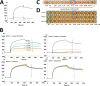
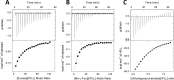
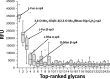
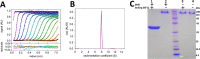
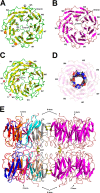
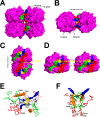
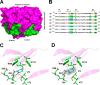
Photorhabdus luminescens is known for its symbiosis with the entomopathogenic nematode Heterorhabditis bacteriophora and its pathogenicity toward insect larvae. A hypothetical protein from P. luminescens was identified, purified from the native source, and characterized as an l-fucose-binding lectin, named P. luminescens lectin (PLL). Glycan array and biochemical characterization data revealed PLL to be specific toward l-fucose and the disaccharide glycan 3,6-O-Me2-Glcβ1-4(2,3-O-Me2)Rhaα-O-(p-C6H4)-OCH2CH2NH2 PLL was discovered to be a homotetramer with an intersubunit disulfide bridge. The crystal structures of native and recombinant PLL revealed a seven-bladed β-propeller fold creating seven putative fucose-binding sites per monomer. The crystal structure of the recombinant PLL·l-fucose complex confirmed that at least three sites were fucose-binding. Moreover, the crystal structures indicated that some of the other sites are masked either by the tetrameric nature of the lectin or by incorporation of the C terminus of the lectin into one of these sites. PLL exhibited an ability to bind to insect hemocytes and the cuticular surface of a nematode, H. bacteriophora.
Keywords: Galleria mellonella; Photorhabdus luminescens; bacterial pathogenesis; crystal structure; hemocytes from insect larvae; host/pathogen interaction; lectin; structural biology.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Joyce S. A., Watson R. J., and Clarke D. J. (2006) The regulation of pathogenicity and mutualism in Photorhabdus. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 9, 127–132 - PubMed
-
- Forst S., Dowds B., Boemare N., and Stackebrandt E. (1997) Xenorhabdus and Photorhabdus spp.: bugs that kill bugs. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 51, 47–72 - PubMed
-
- Duchaud E., Rusniok C., Frangeul L., Buchrieser C., Givaudan A., Taourit S., Bocs S., Boursaux-Eude C., Chandler M., Charles J. F., Dassa E., Derose R., Derzelle S., Freyssinet G., Gaudriault S., et al. (2003) The genome sequence of the entomopathogenic bacterium Photorhabdus luminescens. Nat. Biotechnol. 21, 1307–13 - PubMed
-
- Williamson V. M., and Kaya H. K. (2003) Sequence of a symbiont. Nat. Biotechnol. 21, 1294–1295 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

