Functional architecture of the Reb1-Ter complex of Schizosaccharomyces pombe
- PMID: 27035982
- PMCID: PMC4843429
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1525465113
Functional architecture of the Reb1-Ter complex of Schizosaccharomyces pombe
Abstract
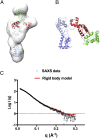
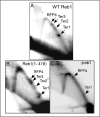
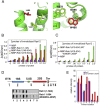
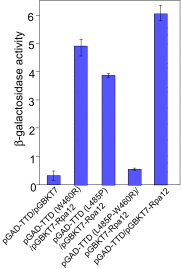
Reb1 ofSchizosaccharomyces pomberepresents a family of multifunctional proteins that bind to specific terminator sites (Ter) and cause polar termination of transcription catalyzed by RNA polymerase I (pol I) and arrest of replication forks approaching the Ter sites from the opposite direction. However, it remains to be investigated whether the same mechanism causes arrest of both DNA transactions. Here, we present the structure of Reb1 as a complex with a Ter site at a resolution of 2.7 Å. Structure-guided molecular genetic analyses revealed that it has distinct and well-defined DNA binding and transcription termination (TTD) domains. The region of the protein involved in replication termination is distinct from the TTD. Mechanistically, the data support the conclusion that transcription termination is not caused by just high affinity Reb1-Ter protein-DNA interactions. Rather, protein-protein interactions between the TTD with the Rpa12 subunit of RNA pol I seem to be an integral part of the mechanism. This conclusion is further supported by the observation that double mutations in TTD that abolished its interaction with Rpa12 also greatly reduced transcription termination thereby revealing a conduit for functional communications between RNA pol I and the terminator protein.
Keywords: RNA polymerase I; crystal structure; protein–DNA interaction; replication termination; transcription termination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Sollner-Webb B, Tower J. Transcription of cloned eukaryotic ribosomal RNA genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:801–830. - PubMed
-
- Reeder RH. Regulation of RNA polymerase I transcription in yeast and vertebrates. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1999;62:293–327. - PubMed
-
- Németh A, et al. RNA polymerase I termination: Where is the end? Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1829(3-4):306–317. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

