Structural and spectroscopic analyses of the sporulation killing factor biosynthetic enzyme SkfB, a bacterial AdoMet radical sactisynthase
- PMID: 30217813
- PMCID: PMC6231123
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005369
Structural and spectroscopic analyses of the sporulation killing factor biosynthetic enzyme SkfB, a bacterial AdoMet radical sactisynthase
Abstract
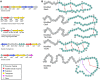
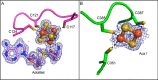
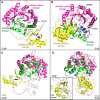
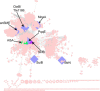
Sactipeptides are a subclass of ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides (RiPPs). They contain a unique thioether bond, referred to as a sactionine linkage, between the sulfur atom of a cysteine residue and the α-carbon of an acceptor residue. These linkages are formed via radical chemistry and are essential for the spermicidal, antifungal, and antibacterial properties of sactipeptides. Enzymes that form these linkages, called sactisynthases, are AdoMet radical enzymes in the SPASM/Twitch subgroup whose structures are incompletely characterized. Here, we present the X-ray crystal structure to 1.29-Å resolution and Mössbauer analysis of SkfB, a sactisynthase from Bacillus subtilis involved in making sporulation killing factor (SKF). We found that SkfB is a modular enzyme with an N-terminal peptide-binding domain comprising a RiPP recognition element (RRE), a middle domain that forms a classic AdoMet radical partial (β/α)6 barrel structure and displays AdoMet bound to the [4Fe-4S] cluster, and a C-terminal region characteristic of the so-called Twitch domain housing an auxiliary iron-sulfur cluster. Notably, both crystallography and Mössbauer analyses suggest that SkfB can bind a [2Fe-2S] cluster at the auxiliary cluster site, which has been observed only once before in a SPASM/Twitch auxiliary cluster site in the structure of another AdoMet radical enzyme, the pyrroloquinoline quinone biosynthesis enzyme PqqE. Taken together, our findings indicate that SkfB from B. subtilis represents a unique enzyme containing several structural features observed in other AdoMet radical enzymes.
Keywords: AdoMet radical enzymes; catalysis; crystal structure; enzyme catalysis; enzyme structure; iron sulfur clusters; metalloenzyme; radical SAM; sactionine linkage; sporulation killing factor.
© 2018 Grell et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures






References
-
- Rea M. C., Sit C. S., Clayton E., O'Connor P. M., Whittal R. M., Zheng J., Vederas J. C., Ross R. P., and Hill C. (2010) Thuricin CD, a posttranslationally modified bacteriocin with a narrow spectrum of activity against Clostridium difficile. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 107, 9352–9357 10.1073/pnas.0913554107 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu W.-T., Yang Y.-L., Xu Y., Lamsa A., Haste N. M., Yang J. Y., Ng J., Gonzalez D., Ellermeier C. D., Straight P. D., Pevzner P. A., Pogliano J., Nizet V., Pogliano K., and Dorrestein P. C. (2010) Imaging mass spectrometry of intraspecies metabolic exchange revealed the cannibalistic factors of Bacillus subtilis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 107, 16286–16290 10.1073/pnas.1008368107 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Datta S., Mori Y., Takagi K., Kawaguchi K., Chen Z.-W., Okajima T., Kuroda S., Ikeda T., Kano K., Tanizawa K., and Mathews F. S. (2001) Structure of a quinohemoprotein amine dehydrogenase with an uncommon redox cofactor and highly unusual crosslinking. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98, 14268–14273 10.1073/pnas.241429098 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

