IP3-mediated gating mechanism of the IP3 receptor revealed by mutagenesis and X-ray crystallography
- PMID: 28416699
- PMCID: PMC5422816
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1701420114
IP3-mediated gating mechanism of the IP3 receptor revealed by mutagenesis and X-ray crystallography
Abstract
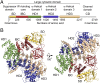
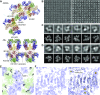
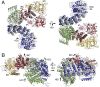
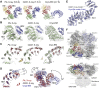
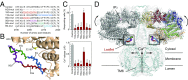
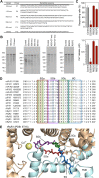
The inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) receptor (IP3R) is an IP3-gated ion channel that releases calcium ions (Ca2+) from the endoplasmic reticulum. The IP3-binding sites in the large cytosolic domain are distant from the Ca2+ conducting pore, and the allosteric mechanism of how IP3 opens the Ca2+ channel remains elusive. Here, we identify a long-range gating mechanism uncovered by channel mutagenesis and X-ray crystallography of the large cytosolic domain of mouse type 1 IP3R in the absence and presence of IP3 Analyses of two distinct space group crystals uncovered an IP3-dependent global translocation of the curvature α-helical domain interfacing with the cytosolic and channel domains. Mutagenesis of the IP3R channel revealed an essential role of a leaflet structure in the α-helical domain. These results suggest that the curvature α-helical domain relays IP3-controlled global conformational dynamics to the channel through the leaflet, conferring long-range allosteric coupling from IP3 binding to the Ca2+ channel.
Keywords: IP3 receptor; X-ray crystallography; allosteric regulation; calcium channel; gating mechanism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Berridge MJ. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993;361:315–325. - PubMed
-
- Mikoshiba K. IP3 receptor/Ca2+ channel: From discovery to new signaling concepts. J Neurochem. 2007;102:1426–1446. - PubMed
-
- Patterson RL, Boehning D, Snyder SH. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors as signal integrators. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004;73:437–465. - PubMed
-
- Furuichi T, et al. Primary structure and functional expression of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-binding protein P400. Nature. 1989;342:32–38. - PubMed
-
- Nishiyama M, Hong K, Mikoshiba K, Poo MM, Kato K. Calcium stores regulate the polarity and input specificity of synaptic modification. Nature. 2000;408:584–588. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

