C-terminal modification of the insulin B:11-23 peptide creates superagonists in mouse and human type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 29255035
- PMCID: PMC5776820
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1716527115
C-terminal modification of the insulin B:11-23 peptide creates superagonists in mouse and human type 1 diabetes
Abstract
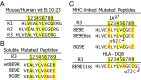
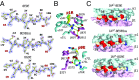
A polymorphism at β57 in some major histocompatibility complex class II (MHCII) alleles of rodents and humans is associated with a high risk for developing type 1 diabetes (T1D). However, a highly diabetogenic insulin B chain epitope within the B:9-23 peptide is presented poorly by these alleles to a variety of mouse and human CD4 T cells isolated from either nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice or humans with T1D. We have shown for both species that mutations at the C-terminal end of this epitope dramatically improve presentation to these T cells. Here we present the crystal structures of these mutated peptides bound to mouse IAg7 and human HLA-DQ8 that show how the mutations function to improve T-cell activation. In both peptide binding grooves, the mutation of B:22R to E in the peptide changes a highly unfavorable side chain for the p9 pocket to an optimal one that is dependent on the β57 polymorphism, accounting for why these peptides bind much better to these MHCIIs. Furthermore, a second mutation of the adjacent B:21 (E to G) removes a side chain from the surface of the complex that is highly unfavorable for a subset of NOD mouse CD4 cells, thereby greatly enhancing their response to the complex. These results point out the similarities between the mouse and human responses to this B chain epitope in T1D and suggest there may be common posttranslational modifications at the C terminus of the peptide in vivo to create the pathogenic epitopes in both species.
Keywords: autoimmunity; peptide presentation; posttranslational modification; self-tolerance.
Copyright © 2017 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Aly TA, et al. Genetic prediction of autoimmunity: Initial oligogenic prediction of anti-islet autoimmunity amongst DR3/DR4-DQ8 relatives of patients with type 1A diabetes. J Autoimmun. 2005;25(Suppl):40–45. - PubMed
-
- Stadinski B, Kappler J, Eisenbarth GS. Molecular targeting of islet autoantigens. Immunity. 2010;32:446–456. - PubMed
-
- Mordes JP, Bortell R, Blankenhorn EP, Rossini AA, Greiner DL. Rat models of type 1 diabetes: Genetics, environment, and autoimmunity. ILAR J. 2004;45:278–291. - PubMed
-
- Concannon P, Rich SS, Nepom GT. Genetics of type 1A diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:1646–1654. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- S10 RR029205/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI018785/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P41 GM103403/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK032083/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR001080/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI018785/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI074491/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK032083/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI018785/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI135374/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI118688/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES025797/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK017047/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

