Structure of the LpxC deacetylase with a bound substrate-analog inhibitor
- PMID: 12833153
- PMCID: PMC6783277
- DOI: 10.1038/nsb948
Structure of the LpxC deacetylase with a bound substrate-analog inhibitor
Abstract
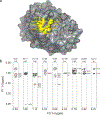
The zinc-dependent UDP-3-O-acyl-N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase (LpxC) catalyzes the first committed step in the biosynthesis of lipid A, the hydrophobic anchor of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) that constitutes the outermost monolayer of Gram-negative bacteria. As LpxC is crucial for the survival of Gram-negative organisms and has no sequence homology to known mammalian deacetylases or amidases, it is an excellent target for the design of new antibiotics. The solution structure of LpxC from Aquifex aeolicus in complex with a substrate-analog inhibitor, TU-514, reveals a novel alpha/beta fold, a unique zinc-binding motif and a hydrophobic passage that captures the acyl chain of the inhibitor. On the basis of biochemical and structural studies, we propose a catalytic mechanism for LpxC, suggest a model for substrate binding and provide evidence that mobility and dynamics in structural motifs close to the active site have key roles in the capture of the substrate.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS STATEMENT
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Figures



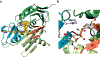

References
-
- Anderson MS, Bulawa CE & Raetz CRH The biosynthesis of Gram-negative endotoxin: formation of lipid A precursors from UDP-GlcNAc in extracts of Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem 260, 15536–15541 (1985). - PubMed
-
- Anderson MS, Robertson AD, Macher I & Raetz CRH Biosynthesis of lipid A in Escherichia coli: identification of UDP-3-O-(R-3-hydroxym yristoyl)-α-D-glucosamine as a precursor of UDP-N2,O3-bis(R-3-hydroxym yristoyl)-α-D-glucosamine. Biochemistry 27, 1908–1917 (1988). - PubMed
-
- Anderson MS et al. UDP-N-acetylglucosamine acyltransferase of Escherichia coli: the first step of endotoxin biosynthesis is thermodynamically unfavorable. J. Biol. Chem 268, 19858–19865 (1993). - PubMed
-
- Young K et al. The envA permeability/cell division gene of Escherichia c li encodes the second enzyme of lipid A biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem 270, 30384–30391 (1995). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
