Usher syndrome type 1-associated cadherins shape the photoreceptor outer segment
- PMID: 28495838
- PMCID: PMC5461027
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201612030
Usher syndrome type 1-associated cadherins shape the photoreceptor outer segment
Abstract
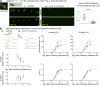
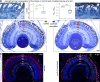
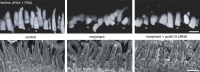
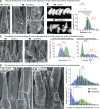
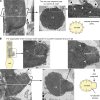
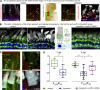
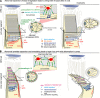
Usher syndrome type 1 (USH1) causes combined hearing and sight defects, but how mutations in USH1 genes lead to retinal dystrophy in patients remains elusive. The USH1 protein complex is associated with calyceal processes, which are microvilli of unknown function surrounding the base of the photoreceptor outer segment. We show that in Xenopus tropicalis, these processes are connected to the outer-segment membrane by links composed of protocadherin-15 (USH1F protein). Protocadherin-15 deficiency, obtained by a knockdown approach, leads to impaired photoreceptor function and abnormally shaped photoreceptor outer segments. Rod basal outer disks displayed excessive outgrowth, and cone outer segments were curved, with lamellae of heterogeneous sizes, defects also observed upon knockdown of Cdh23, encoding cadherin-23 (USH1D protein). The calyceal processes were virtually absent in cones and displayed markedly reduced F-actin content in rods, suggesting that protocadherin-15-containing links are essential for their development and/or maintenance. We propose that calyceal processes, together with their associated links, control the sizing of rod disks and cone lamellae throughout their daily renewal.
© 2017 Schietroma et al.
Figures


References
-
- Alagramam K.N., Yuan H., Kuehn M.H., Murcia C.L., Wayne S., Srisailpathy C.R.S., Lowry R.B., Knaus R., Van Laer L., Bernier F.P., et al. . 2001. Mutations in the novel protocadherin PCDH15 cause Usher syndrome type 1F. Hum. Mol. Genet. 10:1709–1718. (published erratum appears in Hum. Mol. Genet. 2001. 10:2603). 10.1093/hmg/10.16.1709 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bahloul A., Michel V., Hardelin J.P., Nouaille S., Hoos S., Houdusse A., England P., and Petit C.. 2010. Cadherin-23, myosin VIIa and harmonin, encoded by Usher syndrome type I genes, form a ternary complex and interact with membrane phospholipids. Hum. Mol. Genet. 19:3557–3565. 10.1093/hmg/ddq271 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

