Assembly of 500,000 inter-specific catfish expressed sequence tags and large scale gene-associated marker development for whole genome association studies
- PMID: 20096101
- PMCID: PMC2847720
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-1-r8
Assembly of 500,000 inter-specific catfish expressed sequence tags and large scale gene-associated marker development for whole genome association studies
Abstract
Background: Through the Community Sequencing Program, a catfish EST sequencing project was carried out through a collaboration between the catfish research community and the Department of Energy's Joint Genome Institute. Prior to this project, only a limited EST resource from catfish was available for the purpose of SNP identification.
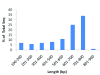
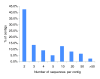
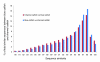
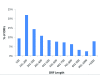
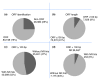
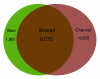
Results: A total of 438,321 quality ESTs were generated from 8 channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) and 4 blue catfish (Ictalurus furcatus) libraries, bringing the number of catfish ESTs to nearly 500,000. Assembly of all catfish ESTs resulted in 45,306 contigs and 66,272 singletons. Over 35% of the unique sequences had significant similarities to known genes, allowing the identification of 14,776 unique genes in catfish. Over 300,000 putative SNPs have been identified, of which approximately 48,000 are high-quality SNPs identified from contigs with at least four sequences and the minor allele presence of at least two sequences in the contig. The EST resource should be valuable for identification of microsatellites, genome annotation, large-scale expression analysis, and comparative genome analysis.
Conclusions: This project generated a large EST resource for catfish that captured the majority of the catfish transcriptome. The parallel analysis of ESTs from two closely related Ictalurid catfishes should also provide powerful means for the evaluation of ancient and recent gene duplications, and for the development of high-density microarrays in catfish. The inter- and intra-specific SNPs identified from all catfish EST dataset assembly will greatly benefit the catfish introgression breeding program and whole genome association studies.
Figures

References
-
- Chatakondi NG, Yant DR, Dunham RA. Commercial production and performance evaluation of channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus female × blue catfish, Ictalurus furcatus male F-1 hybrids. Aquaculture. 2005;247:8.
-
- Peatman E, Baoprasertkul P, Terhune J, Xu P, Nandi S, Kucuktas H, Li P, Wang S, Somridhivej B, Dunham R, Liu Z. Expression analysis of the acute phase response in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) after infection with a Gram-negative bacterium. Dev Comp Immunol. 2007;31:1183–1196. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2007.03.003. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

