Relationship Between Preexisting Cardiovascular Disease and Death and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19
- PMID: 36193749
- PMCID: PMC9575399
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.122.008942
Relationship Between Preexisting Cardiovascular Disease and Death and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19
Abstract
Background: Preexisting cardiovascular disease (CVD) is perceived as a risk factor for poor outcomes in patients with COVID-19. We sought to determine whether CVD is associated with in-hospital death and cardiovascular events in critically ill patients with COVID-19.
Methods: This study used data from a multicenter cohort of adults with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 admitted to intensive care units at 68 centers across the United States from March 1 to July 1, 2020. The primary exposure was CVD, defined as preexisting coronary artery disease, congestive heart failure, or atrial fibrillation/flutter. Myocardial injury on intensive care unit admission defined as a troponin I or T level above the 99th percentile upper reference limit of normal was a secondary exposure. The primary outcome was 28-day in-hospital mortality. Secondary outcomes included cardiovascular events (cardiac arrest, new-onset arrhythmias, new-onset heart failure, myocarditis, pericarditis, or stroke) within 14 days.
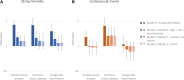
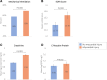
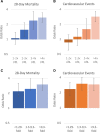
Results: Among 5133 patients (3231 male [62.9%]; mean age 61 years [SD, 15]), 1174 (22.9%) had preexisting CVD. A total of 1178 (34.6%) died, and 920 (17.9%) had a cardiovascular event. After adjusting for age, sex, race, body mass index, history of smoking, and comorbidities, preexisting CVD was associated with a 1.15 (95% CI, 0.98-1.34) higher odds of death. No independent association was observed between preexisting CVD and cardiovascular events. Myocardial injury on intensive care unit admission was associated with higher odds of death (adjusted odds ratio, 1.93 [95% CI, 1.61-2.31]) and cardiovascular events (adjusted odds ratio, 1.82 [95% CI, 1.47-2.24]), regardless of the presence of CVD.
Conclusions: CVD risk factors, rather than CVD itself, were the major contributors to outcomes in critically ill patients with COVID-19. The occurrence of myocardial injury, regardless of CVD, and its association with outcomes suggests it is likely due to multiorgan injury related to acute inflammation rather than exacerbation of preexisting CVD.
Registration: NCT04343898; https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04343898.
Keywords: COVID-19; cardiovascular disease; cardiovascular risk factors; inflammation; troponin.
Figures
References
-
- John Hopkins University Coronavirus Resource Center. COVID-19 United states cases by county by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopskins Univeristy. Available at https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/us-map. Accessed July 14, 2022.
-
- Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the chinese center for disease control and prevention. JAMA. 2020;323:1239–1242. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.2648 - PubMed
-
- Wiersinga WJ, Rhodes A, Cheng AC, Peacock SJ, Prescott HC. Pathophysiology, transmission, diagnosis, and treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review. JAMA. 2020;324:782–793. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.12839 - PubMed
-
- Richardson S, Hirsch JS, Narasimhan M, Crawford JM, McGinn T, Davidson KW, Barnaby DP, Becker LB, Chelico JD, Cohen SL, et al. ; the Northwell COVID-19 Research Consortium. Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York city area. JAMA. 2020;323:2052–2059. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.6775 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

