A functional interleukin 12 receptor complex is composed of two beta-type cytokine receptor subunits
- PMID: 8943050
- PMCID: PMC19484
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.93.24.14002
A functional interleukin 12 receptor complex is composed of two beta-type cytokine receptor subunits
Abstract
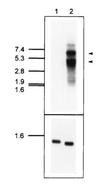
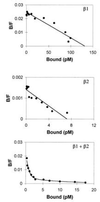
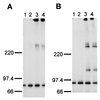
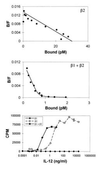
We have identified a cDNA from a human phytohemagglutinin-activated lymphoblast library encoding a protein that binds 125I-labeled human interleukin 12 (125I-huIL-12) with a Kd of about 5 nM when expressed in COS-7 cells. When coexpressed in COS-7 cells with the previously identified IL-12 beta receptor (IL-12R beta) protein, two classes of 125I-huIL-12 binding sites were measured with Kds of about 55 pM and 8 nM, corresponding to the high- and low-affinity binding sites seen on phytohemagglutinin-activated lymphoblasts. This newly identified huIL-12R subunit is a member of the cytokine receptor superfamily, with closest resemblance to the beta-type cytokine receptor gp130 and the receptors for leukemia inhibitory factor and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Consequently, we have reclassified the previously identified IL-12R beta subunit as huIL-12R beta 1 and designated the newly identified subunit as huIL-12R beta 2. huIL-12R beta 2 is an 862-amino acid type I transmembrane protein with a 595-amino-acid-long extracellular domain and a cytoplasmic tail of 216 amino acids that contains three tyrosine residues. A cDNA encoding the mouse homolog of the huIL12R beta 2 protein has also been isolated. Human and mouse IL-12R beta 2 proteins show a 68% amino acid sequence identity. When expressed in COS-7 cells, huIL-12R beta 2 exists as a disulfide-linked oligomer with an apparent monomeric molecular weight of 130 kDa. Coexpression of the two identified IL-12R subunits in Ba/F3 cells conferred IL-12 responsiveness, and clones of these cotransfected Ba/F3 cells that grew continuously in the presence of IL-12 were isolated and designated LJM-1 cells. LJM-1 cells exhibited dose-dependent proliferation in response to huIL-12, with an ED50 of about 1 pM huIL-12. Interestingly, Ba/F3 cells transfected with IL-12R beta 2 alone proliferated in response to huIL-12 with an ED50 of about 50 pM, although a role for endogenous mouse IL-12R beta 1 in IL-12 signal transduction in these transfectants cannot be ruled out. These results demonstrate that the functional high-affinity IL-12R is composed of at least two beta-type cytokine receptor subunits, each independently exhibiting a low affinity for IL-12.
Figures
References
-
- Wolf S F, Temple P A, Kobayashi M, Young D, Dicig M, Lowe L, Dzialo R, Fitz L, Ferenz C, Hewick R M. J Immunol. 1991;146:3074–3081. - PubMed
-
- Gately M K, Desai B B, Wolitzky A G, Quinn P M, Dwyer C M, Podlaski F J, Familletti P C, Sinigaglia F, Chizzonite R, Gubler U. J Immunol. 1991;147:874–882. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

