Ixekizumab, an interleukin-17A specific monoclonal antibody, for the treatment of biologic-naive patients with active psoriatic arthritis: results from the 24-week randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled and active (adalimumab)-controlled period of the phase III trial SPIRIT-P1
- PMID: 27553214
- PMCID: PMC5264219
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209709
Ixekizumab, an interleukin-17A specific monoclonal antibody, for the treatment of biologic-naive patients with active psoriatic arthritis: results from the 24-week randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled and active (adalimumab)-controlled period of the phase III trial SPIRIT-P1
Abstract
Objective: To assess the safety and efficacy of ixekizumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits interleukin-17A, in a double-blind phase III trial enrolling patients with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
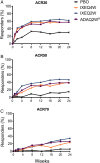
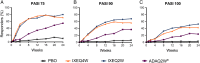
Methods: Patients naive to biologic therapy with active PsA were randomised to subcutaneous injections of placebo (N=106), adalimumab 40 mg once every 2 weeks (active reference; N=101), ixekizumab 80 mg once every 2 weeks (IXEQ2W) (N=103), or ixekizumab 80 mg once every 4 weeks (IXEQ4W) (N=107). Both ixekizumab regimens included a 160-mg starting dose. The primary objective was to assess the superiority of IXEQ2W or IXEQ4W versus placebo as measured by the proportion of patients achieving an American College of Rheumatology 20 (ACR20) response at week 24.
Results: Significantly more patients treated with ixekizumab achieved an ACR20 response with IXEQ2W (62.1%) or IXEQ4W (57.9%) than placebo (30.2%) (p≤0.001; non-responder imputation method). Disease activity and functional disability were significantly improved with both ixekizumab doses versus placebo at weeks 12 and 24, and there was significantly less progression of structural damage at week 24 (p≤0.01). Clearance of plaque psoriasis was greater with ixekizumab than placebo (p≤0.001). Efficacy results with adalimumab, the active reference arm, showed significant improvements versus placebo. Treatment-emergent adverse events were more frequent with ixekizumab (65.7-66.4%) and adalimumab (64.4%) than placebo (47.2%) (p<0.05).
Conclusions: In biologic-naive patients with active PsA, ixekizumab treatment resulted in improvements in disease activity and physical function, as well as in the inhibition of structural damage progression. Overall, adverse events were more frequent in all active groups compared with placebo.
Trial registration number: NCT01695239; EudraCT2011-002326-49; Results.
Keywords: DMARDs (biologic); Psoriatic Arthritis; Spondyloarthritis; Treatment.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/.
Conflict of interest statement
PJM reports grants and personal fees from Eli Lilly & Company during the conduct of the study. PJM also reports, outside the submitted work, grants, personal fees, and non-financial support from AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Crescendo, Genentech, Janssen, Pfizer and UCB Pharma; grants and personal fees from Merck and Novartis; and non-financial support from Corrona. DvdH reports personal fees from Eli Lilly & Company, during the conduct of the study. DvdH also reports personal fees from AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Augurex, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Centocor, Chugai, Covagen, Daiichi, Galapagos, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Otsuka, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi-Aventis, UCB Pharma and Vertex, outside the submitted work. DvdH is the director at Imaging Rheumatology BV. CTR reports personal fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Janssen, Novartis, UCB, Boerhinger Ingelheim, as well as grants from Amgen, outside the submitted work. MO reports grants and non-financial support from Eli Lilly & Company, during the conduct of this study. MO also reports non-financial support from Santen Pharmaceutical, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Pfizer and Abbott Japan, outside the submitted work. RSC and DKB were employees of Eli Lilly & Company, at the time this study was conducted. CLS, C-YL and CHL are employees of Eli Lilly & Company. DDG reports grants and personal fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Celgene, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB, and personal fees from Eli Lilly & Company, outside the submitted work.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

